Forschung
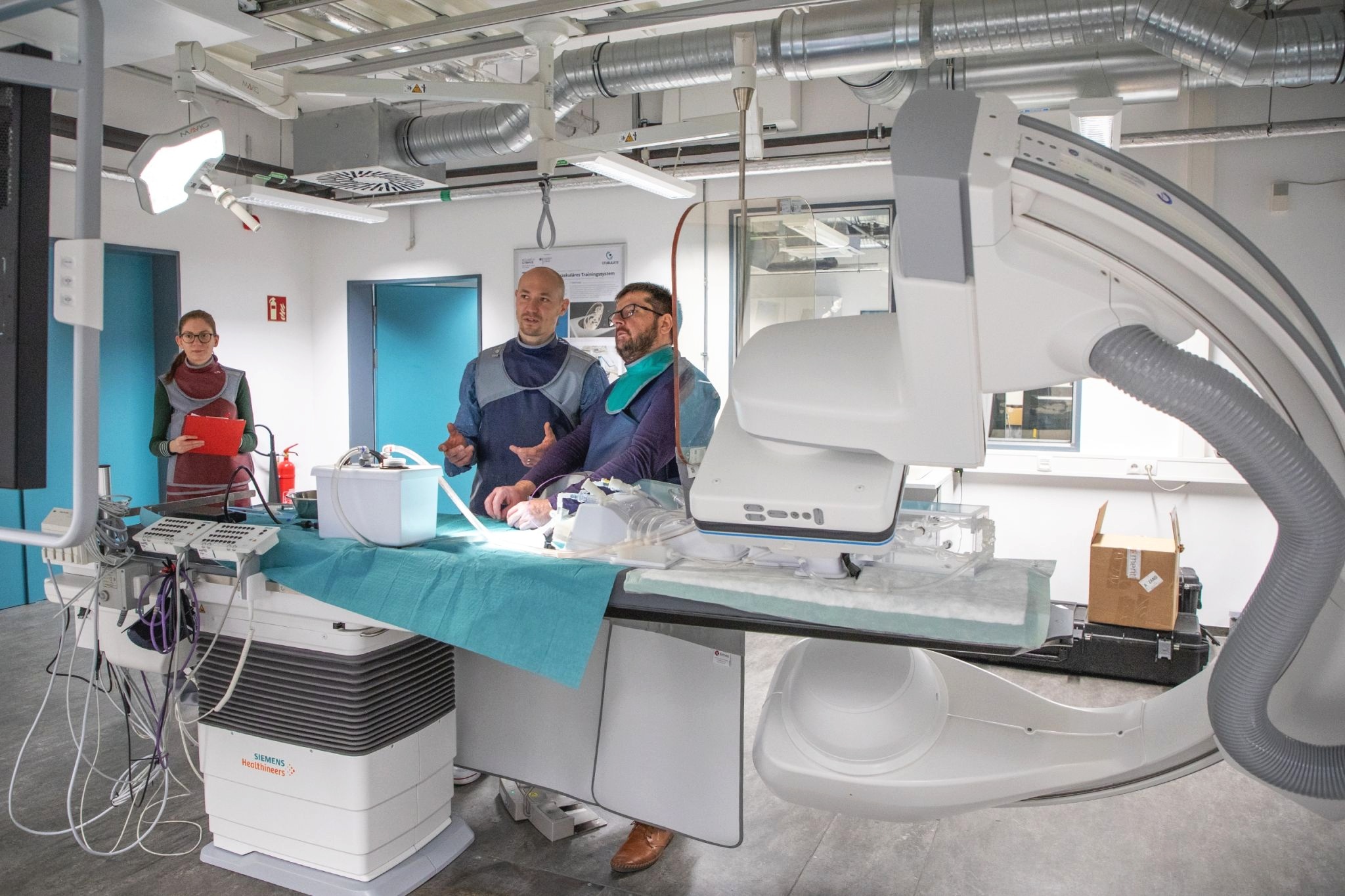
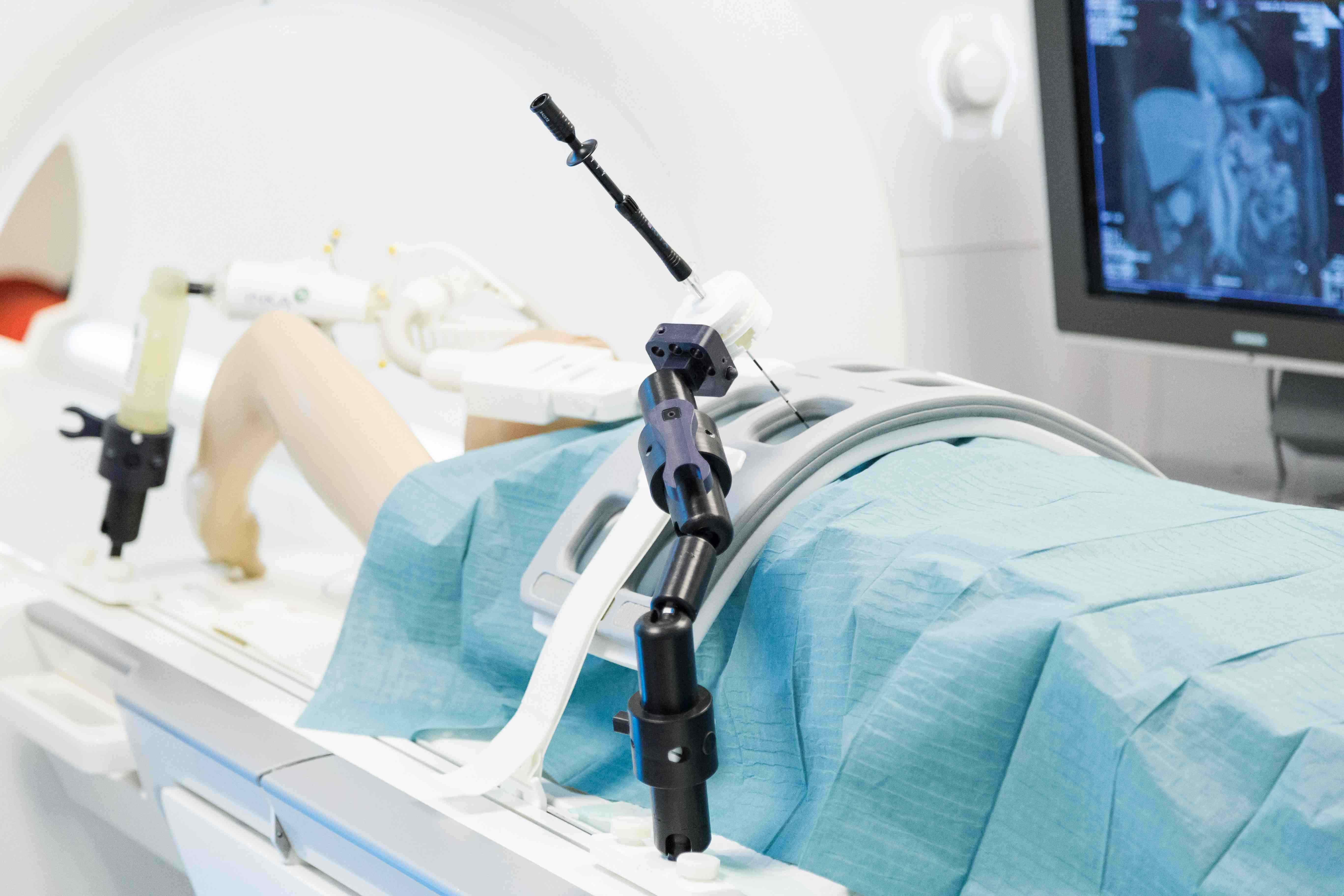
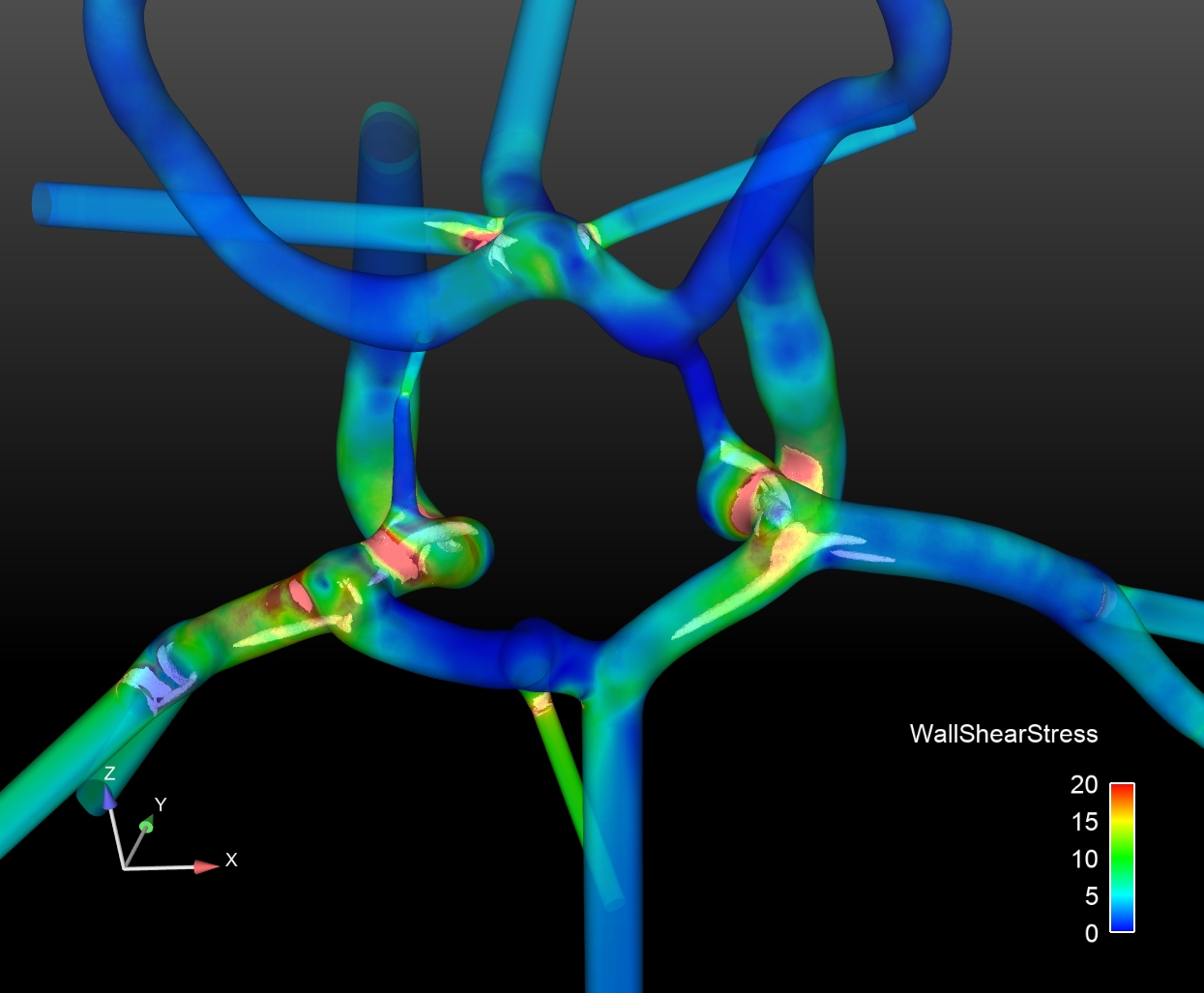
Am Forschungscampus STIMULATE werden Lösungen und Technologien für hochinnovative Therapie- und Diagnoseverfahren der bildgeführten minimal-invasiven Medizin entwickelt. In interdisziplinärern Teams aus Klinik, Industrie und Wissenschaft forschen und entwickeln wir Hand in Hand.
Mehr erfahren